Match Tomato Fertilizer Products and Nutrition Plan to Growth Needs
Tomato is a versatile crop grown worldwide in diverse environments, from open fields to greenhouses. This adaptability requires adjusting fertilization to their specific growth conditions.
Tomatoes thrive in well-drained soils and prefer warm climates (18-27°C). While moderately drought-resistant, tomatoes require proper water management for optimal yield and quality. Outdoor plants need 4,000-6,000 m³/ha, while greenhouses can require up to 10,000 m³/ha.

Tomato growth patterns
Tomato cultivars are classified into three major groups by their growth patterns: determinate, indeterminate, and semi-determinate. The plant growth pattern determines the dynamics of nutrient requirements throughout the crop’s growth cycle.
Determinate varieties have a limited growth habit. The main and side stems stop growing after producing a predetermined number of inflorescences (clusters of flowers).
Indeterminate varieties have unlimited growth habit. The main and side stems continue to grow and produce flowers and fruit indefinitely.
Semi-determinate varieties are hybrids of determinate and indeterminate tomatoes. They have a limited growth habit, but they continue to produce flowers and fruit for a longer period than determinate tomatoes.
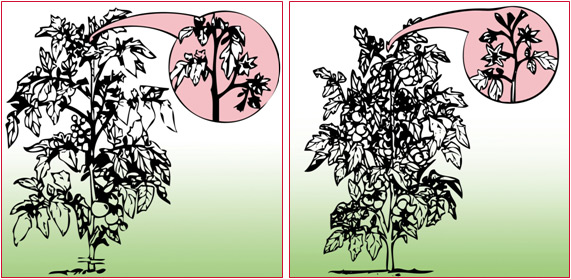
Determinate (left) and indeterminate (right) tomato growth
Tomato growth stages
The lifecycle of the tomato plant can be split roughly into four periods:
- Establishment - from planting or seeding through vegetative growth until first flower appears
- From first flowering to first fruit set
- From fruit ripening to first harvest
- From first harvest to the end of last harvest
Development of the tomato fruit
After fruit setting, fruit ripens over a period of 45-70 days, depending upon the cultivar, climate and growth conditions. Fruit expansion continues until the stage of green ripeness.
Ripening occurs as the fruit changes color from light green to off-white, pink, red, and finally dark red or orange. Depending on the distance and time to market, yield may be harvested at any time between the pink to dark red stage, the later stages producing fruits richer in flavor.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Breaker | Red stains appear on fruit skin |
| Pink | Tomato turns pink, not yet ready for consumption |
| Red | The tomato is red and completely ripe for consumption |





