Index:
- Mineral nutrition of strawberries with fully soluble fertilizers
- Soil-grown strawberries with expected yield of 25 MT/ha
- High-tunnel, soil grown strawberries with expected yield of 50 MT / ha
- Green-house, soilless grown strawberries with expected yield of 60 MT / ha
- 6.2 Controlled release nutrition of strawberries
- Multicote™ Agri for strawberries
- Worldwide fertilization practices with Multicote™Agri
- Fertilization
- Pre-plant fertilization
- Fertilization of winter crop
- Fertilization of a summer crop
Please note that the following recommendations should be used as guidelines only, as the real applications are dependent also on many local conditions that can have a crucial effect on the plantation performance, e.g., cultivar, planting season, individual growth stage durations, ambient temperature, soil fertility, mineral contents of irrigation water, etc.
Soil type: sandy loam ; Irrigation method: above canopy sprinklers
Base dressing
|
Fertilizer
|
Rate (kg / ha)
|
|
Ammonium nitrate (34% N)
|
130
|
|
Superphosphate (25% P2O5)
|
400
|
|
Potassium sulfate (50% K2O)
|
364
|
|
Dolomite (26% CaO)
|
131
|
|
Magnesium sulfate (16% MgO)
|
81
|
Side dressing
|
Growth stage
|
Days per growth stage
|
Fertilization during growth stage (kg / ha)
|
|
|
Ammonium nitrate
|
Multi-K+ME
|
||
|
Planting: October 15
|
|
---
|
---
|
|
Establishment, until November 15
|
30
|
85
|
65
|
|
Growth, until January 8
|
55
|
---
|
---
|
|
First flowering: January 8
|
5
|
---
|
---
|
|
First flowering: January 8
|
5
|
---
|
---
|
|
Growth of 1st fruit wave, until February 28
|
45
|
110
|
60
|
|
Growth of 2nd fruit wave, until April 5
|
36
|
---
|
---
|
|
Growth of 3rd fruit wave, until April 30
|
25
|
85
|
80
|
|
Growth of 4th fruit wave, until May 31
|
30
|
---
|
---
|
|
Total for season
|
226
|
280
|
205
|
Foliar feeding
None.
6.1.2 Soil grown strawberries with expected yield of 40 MT / ha
Soil type: sandy loam
Irrigation method: drip
|
Fertilizer
|
Rate (kg / ha)
|
|
Ammonium nitrate (34% N)
|
197
|
|
Superphosphate (25% P2O5)
|
308
|
|
Potassium sulfate (50% K2O)
|
316
|
|
Dolomite (26% CaO)
|
162
|
|
Magnesium sulfate (16% MgO)
|
100
|
Side dressing by Nutrigation™
|
Growth stage
|
Days per growth stage
|
Fertilization during growth stage (kg / ha)
|
||||
|
Ammonium nitrate
|
Haifa MAP™
|
Multi-K™ GG
|
Haifa Cal™ Nutrigation™ Grade
|
Magnisal™
|
||
|
Planting: Oct. 15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Establishment, until Nov. 15
|
30
|
40
|
25
|
80
|
5
|
3
|
|
Growth, until Jan. 8
|
55
|
30
|
20
|
80
|
5
|
3
|
|
First flowering: Jan. 8
|
5
|
--
|
15
|
20
|
--
|
--
|
|
Growth of 1st fruit wave, until Feb. 28
|
45
|
35
|
10
|
110
|
10
|
7
|
|
Growth of 2nd fruit wave, until Apr. 10
|
41
|
35
|
5
|
130
|
10
|
7
|
|
Growth of 3rd fruit wave, until May 5
|
25
|
30
|
5
|
80
|
8
|
5
|
|
Growth of 4th fruit wave, until June 10
|
35
|
30
|
5
|
15
|
--
|
--
|
|
Total for season
|
236
|
200
|
85
|
515
|
38
|
25
|
Haifa MAP™: 12-61-0, fully soluble Mono-ammonium phosphate.
Multi-K™ GG: 13.5-0-46.2, fully soluble potassium nitrate.
Haifa Cal™ GG: 15.5-0-0+ 26.5 CaO, fully soluble calcium nitrate.
Magnisal™: 11-0-0+ 16 MgO, fully soluble magnesium nitrate.
Foliar feeding
In mid-November: Poly-Feed™ Foliar21-21-21 with micronutrients
Soil type: sandy loam
Irrigation method: dripping
|
Fertilizer
|
Rate (kg / ha)
|
|
Ammonium nitrate (34% N)
|
233
|
|
Superphosphate (25% P2O5)
|
344
|
|
Potassium sulfate (50% K2O)
|
376
|
|
Dolomite (26% CaO)
|
192
|
|
Magnesium sulfate (16% MgO)
|
119
|
Side dressing by Nutrigation™
|
Growth stage
|
Days per growth stage
|
Fertilization during growth stage (kg / ha)
|
||||
|
Ammonium nitrate
|
Haifa MAP™
|
Multi-K™ GG
|
Haifa Cal™Nutrigation™ Grade
|
Magnisal™
|
||
|
Planting: Oct. 15
|
|
47
|
29
|
95
|
6
|
6
|
|
Establishment, until Nov. 15
|
30
|
35
|
22
|
95
|
6
|
6
|
|
Growth, until Jan. 8
|
55
|
|
17
|
24
|
|
|
|
First flowering: Jan. 8
|
5
|
42
|
11
|
131
|
12
|
12
|
|
Growth of 1st fruit wave, until Feb. 28
|
45
|
42
|
6
|
156
|
12
|
12
|
|
Growth of 2nd fruit wave, until Apr. 10
|
41
|
36
|
5
|
95
|
10
|
10
|
|
Growth of 3rd fruit wave, until May 5
|
25
|
35
|
5
|
19
|
|
|
|
Growth of 4th fruit wave, until June 10
|
35
|
47
|
29
|
95
|
6
|
6
|
|
Total for season
|
236
|
237
|
95
|
615
|
46
|
31
|
Haifa MAP™: 12-61-0, fully soluble mono-ammonium phosphate.
Multi-K™ GG: 13.5-0-46.2, fully soluble potassium nitrate.
Haifa Cal™ GG: 15.5-0-0+ 26.5 CaO, fully soluble calcium nitrate.
Magnisal™: 11-0-0+ 16 MgO, fully soluble magnesium nitrate.
Foliar feeding
1. In mid-November: Poly-Feed™ Foliar 21-21-21, with micronutrients, at 0.5%
2. In February: Poly-Feed™ Foliar16-7-30+2MgO, with micronutrients, at 0.5% to 1%
Soil type: sandy loam
Irrigation method: dripping
Nutrigation
|
Growth stage
|
Days per growth stage
|
Fertilization during growth stage (kg / ha)
|
||||
|
Ammonium nitrate
|
Haifa MAP™
|
Multi-K™ GG
|
Haifa Cal™ Nutrigation™ Grade
|
Magnisal™
|
||
|
Planting: Oct. 15
|
|
10
|
20
|
30
|
10
|
8
|
|
Establishment, until Nov. 15
|
30
|
40
|
45
|
80
|
20
|
15
|
|
Growth, until Jan. 8
|
55
|
40
|
37
|
150
|
50
|
40
|
|
First flowering: Jan. 8
|
5
|
|
5
|
15
|
10
|
5
|
|
Growth of 1st fruit wave, until Feb. 28
|
45
|
10
|
50
|
370
|
48
|
30
|
|
Growth of 2nd fruit wave, until Apr. 10
|
41
|
10
|
42
|
310
|
50
|
30
|
|
Growth of 3rd fruit wave, until May 5
|
25
|
16
|
27
|
140
|
45
|
20
|
|
Growth of 4th fruit wave, until June 10
|
35
|
25
|
30
|
55
|
36
|
21
|
|
Total for season
|
236
|
151
|
256
|
1,150
|
269
|
169
|
Haifa MAP™: 12-61-0, fully soluble mono-ammonium phosphate.
Multi-K™ GG: 13.5-0-46.2, fully soluble potassium nitrate.
Haifa Cal™ GG: 15.5-0-0+ 26.5 CaO, fully soluble calcium nitrate.
Magnisal™: 11-0-0+ 16 MgO, fully soluble magnesium nitrate.
Foliar feeding
-
In mid-November: Poly-Feed™ Foliar 21-21-21, with micronutrients, at 0.5%
-
In February : Poly-Feed™ Foliar 16-7-30+2MgO, with micronutrients, at 0.5-1%
-
In mid-March: Poly-Feed™ Foliar 16-7-30+2MgO, with micronutrients, at 0.5-1%
6.2.1 Multicote™ Agri Controlled Release Fertilizers technology
Multicote™ Agri is a controlled-release fertilizer, designed to release available nutrients to the soil solution slowly and continuously over months. Multicote™ Agri is made of polymer-coated fertilizer granules. Following application, the granules start absorbing soil moisture that dissolves the granule cores that are made of a soluble fertilizer mini-granule. The dissolved nutrients then diffuse, slowly and continuously, into the root zone. The release rate depends upon, and is dictated solely by the soil temperature and the granule coating pore size. The release rate increases as temperature rises, which coincides with plant uptake rates as a function of temperature. Other factors, such as soil type, humidity, pH, and microbial activity do not affect the release rate. Multicote™Agri products also contain non-coated, readily available nutrients, for establishment and initial growth.
The advantages Multicote™ Agri:
-
Nutrients are supplied in accordance with plant needs, for optimal development and best yields.
-
Single application per season, which results in a drastic reduction of field labor and application costs, as well as considerably less soil compaction.
-
Minimized losses through leaching, volatilization or fixation in the soil, without compromising on nutrient availability throughout the growth season.
-
More efficient use of fertilizers without wastage enables reduced application rates.
-
Ecologically superior (no soil or air pollution).
Multicote™ Agri release mechanism
Multicote™ Agri is based on polymer-coated fertilizer granules. During the production process, water-soluble nutrients are encapsulated in a polymeric shell. This shell prevents the immediate dissolution of the fertilizer when applied to the soil. The thickness of the shell determines the longevity of nutrient release. See Figure 6.1a.
Following application, soil moisture slowly penetrates through the coating. This moisture starts a gradual dissolution of the nutrients inside the granule. See Figure 6.1b.
The dissolved nutrients diffuse through the coating to the root zone, providing the plant with available nutrients in measured portions according to its growth needs. See Figure 6.1c.
The diffusion rate, which is the actual release rate, is dictated solely by the soil temperature. The release rate increases as temperature rises.
While nutrients are released to the root zone, further penetration of moisture dissolves more of the solid fertilizer. At a certain stage, the entire content of the granule is dissolved, ready for diffusion and release. Starting at this stage the release rate slows down. See Figure 6.1d.
After the release is complete, the empty shell ruptures and degrades, leaving no residues in the soil. See Figure 6.1e.
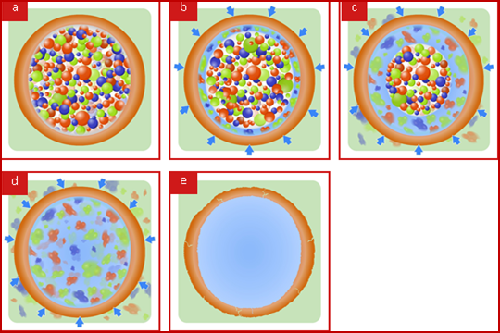
Figure 6.1: Multicote™Agri release mechanism
Haifa offers worldwide strawberry growers Multicote™ Agri formulae specially tailored to suit local cultivars and growth conditions. Multicote™ Agri formulae for strawberries may consist of either 100% polymer coated fertilizer granules, or, for cost-saving reasons and / or to meet local specific plant nutrient requirements, it may partially contain also non-coated, readily available fertilizers.
The versatile controlled release characteristics of Multicote™ Agri give growers the power to apply a cost effective fertilizer, a suitable product for each strawberry growth area.
Multicote™ Agri minimizes nutrient loss, gives strawberries the right amount of nutrients, and helps strawberry growers maximize profitability.
The Multicote™ Agri granules are banded in a planting slot 15 cm to 20 cm (6 inches to 8 inches) deep. The total rate of fertilizer applied depends on the type of materials used and the residual nutrient levels in the soil.
Shortly after the granule application the strawberry roots identify the granules as a source of beneficial nutrients, and new, efficient roots are formed near the granules to take advantage of their contents. See Figures 6.2.


Figure 6.2: A strawberry plant dug out to demonstrate grain application location, and the dense net of newly formed roots around the Multicote™ Agri granules
Israel
Soil type: light textured soil
Planting time: early to late fall
Growing method: mainly plasticulture; covered with mini- or high-tunnels
Recommended plant nutrients for 7 to 8 month growth period (kg / ha)
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
CaO
|
MgO
|
|
220 -250
|
120– 130
|
350– 370
|
200– 250
|
100– 120
|
Application rates of N & K throughout growth stages (kg / ha / week)
|
|
Nov.
|
Dec.
|
Jan.
|
Feb.
|
March
|
|
N
|
7.5
|
11
|
7
|
11 – 14.5
|
11
|
|
K2O
|
-
|
17.5
|
11
|
17.5 – 21
|
17.5
|
Nitrogen, after transplanting is supplied with the first fertigation.
Phosphorus: Applying 500 to 1,000 kg / ha of triple superphosphate (46% P2O5).
Potassium: Applying 500 kg / ha of potassium chloride 60% K2O.
Side / top-dressing with Multicote™ Agri:
The required plant nutrients are supplied by Multicote™ Agri (6 months) 17-8-27 orMulticote™Agri Multicote™ Agri (6 months) 15-5-30 (90%-50%-90%, respectively, polymer coated), at a rate of 800 to 1,000 kg / ha. This Multicote™ Agri application results in higher yield of better quality fruits.
There are three application methods:
-
Broadcasting on the bed, before planting, and incorporating with a rototiller.
-
Banding Multicote™ Agri between two planted rows, next to the irrigation line.
-
Broadcasting after plants are established, before mulching with plastic, and incorporating with a suitable cultivator. This method is the most popular type of application.
The normal yield of a field planted in mid-October and harvested until the end of May, is 70 to 75 MT / ha in mini-tunnels and 75 to 80 MT / ha in high tunnels. It is distributed between the months shown in Table 6.1.
Table 6.1: Average yield (MT / ha) during the growth period
|
|
Nov.
|
Dec.
|
Jan.
|
Feb.
|
March
|
April
|
May
|
Total
|
|
Export quality
|
0
|
5
|
2
|
5
|
3
|
0
|
0
|
15
|
|
Local market
|
0
|
3
|
3
|
7
|
10
|
12
|
10
|
45
|
|
Total
|
0
|
8
|
5
|
12
|
13
|
12
|
10
|
60
|
South Africa
Soil type: Sandy, in some cases sandy-loam
Growing period: Planting in March / April (autumn), harvesting: June to December
Normal yield: 40 to 50 MT / ha
Growing method: Multi-span tunnels and open fields with mini-tunnels during the winter months. The objective is to grow a fair-sized plant, not overly vegetative, that continuously flowers and sets fruit. The fertigation solution is adjusted during the season using soil solution and leaf analysis, as well as visual observation. Irrigation is by means of single dripper line with a 35 cm dripper-spacing.
Fertilization
The seasonal plant nutrient application (kg / ha) is about:
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
|
200
|
100
|
300
|
Pre-plant applications:
-
Lime and / or gypsum are applied prior to ridge formation; rate is based on soil analysis.
-
Multicote™ Agri (6) 17-8.5-26 (80-100-100% polymer coated) @ 1,100 kg / ha.
Post planting, calcium nitrate is applied throughout the season by fertigation at a rate of 40 ppm. Additional Multi-K™ is applied at the final stages of the season to stretch the growing season and maintain fruit quality as long as possible. Whenever needed, Multicote™ Agri may contain also Mg and micronutrients.
Application method
The fertilizer is banded by a Monosem fertilizer applicator mounted on the ridger. A single band of fertilizer is placed between two rows of plants on each ridge. See Figure 6.3.

Figure 6.3: A ‘Monosem’ fertilizer applicator mounted on the ridger.Multicote™ Agri applied simultaneously with bed preparation
California, USA
Soil type: Sand / sandy-loam to loamy clay soil
Growing period: Winter: October to May; Summer: July to December
Growing method: Open field, plastic mulch
Recommended plant nutrients for Southern California
The seasonal plant nutrient application (kg / ha) is about:
|
kg / ha
|
lbs / acres
|
||||
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
|
225
|
90
|
160
|
200
|
80
|
140
|
Normalyield: 67 MT / ha (30 ton / acre or 5,000 trays per acre)
Pre-plant: 15-15-15 or 16-20-0 at: 225 to 334 kg / ha (200 to 300 lb / acre), plus Multicote™ Agri 22-8-13 at 900 to 1,100 kg / ha (800 to 1,000 lbs / acre), 100% polymer coated
Recommended plant nutrients for Northern California
|
kg / ha
|
lbs / acres
|
||||
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
|
110
|
45
|
70
|
100
|
40
|
60
|
Normal yield: 78 ton / ha (35 ton / acre or 5833 trays per acre)
Pre-plant: Multicote™ Agri 22-8-13 at 530 kg / ha (475 lbs / acre), 100% polymer coated
Application method
Multicote™ Agri is applied in a tight band by ‘Clampco’ shank (see Figure 6.4 to Figure 6.6) and placed precisely in the fertilizer slot, at least 4 cm (1.5 inches) off the transplant roots of two-row beds

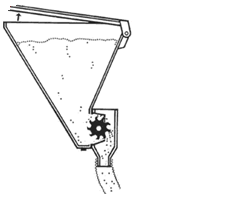
Figure 6.4: ‘Clampco’ precision applicator provides free flow of Multicote™ Agri

Figure 6.5: A two-row ‘Clampco’ applicator, banding Multicote™ Agri
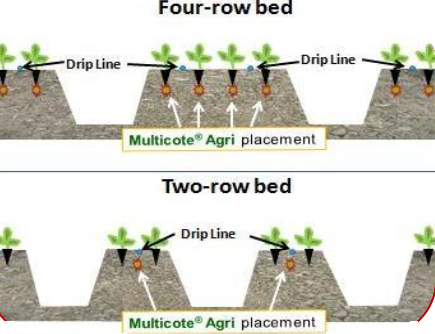
Figure 6.6: Two- or four-row bed planting and Multicote™ Agri placement patterns in California strawberry
Normal yield: 34 ton / ha (15 ton / acre)
Pre-plant fertilization is not practiced.
-
CAN solution of 15% to 17% N is applied monthly at an application rate of 280 to 470 L / ha (30 to 50 gal / acre).
-
White (technical grade, 75% P2O5) phosphoric acid is applied ~45 days after planting, at a rate of 470 L / ha (50 gal / acre).
-
During the first two months after planting, a solution of 4-10-10+ME, made from Multi-K™ is fertigated four times a month. Standard rates are 4 to 11 kg N / ha / application (3 to 10 lbs N / acre / application) or at a rate of 50 to 100 L / ha (5 to 10 gal / acre).
-
At the end of the season, 2-18-18 analysis, for juice and freezer berries, may be applied.
-
Liquid feed is also applied right after rain, depending on amount of rainfall.


Figure 6.7: Mulched strawberry in open-field in southern California
Mexico – Baja California
Soil type: Medium to light textured
Growing period: Transplanting - September to mid October, harvesting ends in May
Growing method: Similar to southern California; 2 or 4 rows / mulched bed
Fertilization
Base-dressing, similar to Californian practice. During bed preparation, Multicote™ Agri (6) 22-8-13 is applied at 800 to 1,200 kg / ha before transplanting.
Fruit quality
Highest fruit quality is harvested between December and February. Lower quality is harvested between March and June.
Central Mexico – Inland
Soil type: Medium to heavy textured
Growing method: Open field is practiced by 70% of the growers.
Growth period: Transplanting in August / September; harvesting ends in April / May.
Inundation: It is a common practice is to flood the field between growth seasons in order to control weeds and soil-borne diseases (see Figure 6.8). The flooding lasts between 1 and 3 months.

Figure 6.8: Flooded field
Soil preparation: Beds are prepared in May, sometimes with base-dressing incorporation. Some growers apply fertilizers only after transplanting in September.
Transplanting: In August and September, immediately after draining the flooded field.
Fertilization
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
CaO
|
MgO
|
|
kg / ha
|
||||
|
185
|
160
|
320
|
85
|
When needed
|
Application methods
-
Traditional methodCommon N-P-K fertilizers, such as: 12-11-17, 15-15-15, etc., are applied in two sessions after transplanting.The first application takes place 20 to 25 days after transplantation, and second application takes place 60 to 65 days after transplantation. However, part of the required plant nutrients are sometimes also applied as base-dressing.
-
Advanced methodMulticote™ Agri (8) 12-15-17 (30%-0%-30% polymer coated), at a rate of 500 kg / ha is applied in September / October, 20 to 25 days after transplanting, once only, either manually (Figure 6.9) or by a mechanical applicator (Figure 6.10). This application method eliminates the need to top-dress at a later stage.

Figure 6.9: Multicote™ Agri, manually applied

Figure 6.10: Multicote™ Agri, mechanically applied
Fertigation
During all growing stages, strawberries are fertigated with water-soluble fertilizers.
Harvesting
Harvest is done once every 3 days, up to 60 to 70 harvests during the crop cycle, until the end of May. The highest quality fruit is obtained during February to April.
Normal yield
45 to 55 MT / ha
Central Mexico – inland
Soil type: Medium to heavy textured
Growing method: Macro-tunnels are practiced by 30% of the growers
Field preparation: Starts in May, soil is base-dressed, and then beds are mulched with plastic.
Macro-tunnels
Tunnels are installed before the rainy season. In the past, it was common practice to flood the field (Figure 6.11) to control weeds and pests. Today, most growers use pesticides and herbicides for this purpose.

Figure 6.11: A flooded macro-tunnel

Figure 6.12: A macro-tunnel fertilized with Multicote™ Agri
Growing period: Early August / September; end of the harvest March to mid-May
Transplantation: The transplanting process starts after draining the flooded field, in August.
Fertilization: After bed preparation and mulching, Multicote™ Agri (8) 15-15-15 (100%-0%-100% polymer coated) is applied at a rate of 400 kg / ha (Figure 6.10).
Normal yield: 65 to 75 MT / ha. Harvest is done once every 3 days, up to 60 to 70 harvests during the crop cycle, until the end of May.
Spain
Soil type: Sandy soil with high pH around 7 to 8
Growing period: Planting in April; end of harvest in October
Growing method: Open field, no mulch, irrigated by sprinklers
Fertilization
Recommended plant nutrients for the entire growth period (kg / ha):
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
|
140
|
60
|
50
|
Pre-plant fertilization
Multicote™ Agri (4) 15-15-15+1,2 MgO or Multicote™ Agri (4) 18-11-11+4 MgO, at 20 to 30 g / linear meter
Side-dressing: 11 weeks after planting, weekly fertigation sessions from June to September, with water-soluble fertilizer, such as: Poly-Feed™ 22-0-10+3MgO + MAP

Figure 6.13: Transplanting and application of Multicote™ Agri

Figure 6.14: Initial growth stage of the field
Need more information about growing strawberries? You can always return to the strawberry fertilizer & strawberry crop guide table of contents



